Step 1: Download the files
Download the latest PHP 5 ZIP package from www.php.net/downloads.php
As always, virus scan the file and check its MD5 checksum using a tool such as fsum.
Step 2: Extract the files
We will install the PHP files to C:\php, so create that folder and extract the contents of the ZIP file into it.
PHP can be installed anywhere on your system, but you will need to change the paths referenced in the following steps.
Step 3: Configure php.ini
Copy C:\php\php.ini-development to C:\php\php.ini. There are several lines you will need to change in a text editor (use search to find the current setting). Where applicable, you will need to remove the leading semicolon to uncomment these setting.
Define the extension directory:
extension_dir = "C:/php/ext"
Enable extensions. This will depend on the libraries you want to use, but the following extensions should be suitable for the majority of applications:
extension=curl
extension=gd2
extension=mbstring
extension=mysql
extension=pdo_mysql
extension=xmlrpc
If you want to send emails using the PHP mail() function, enter the details of an SMTP server (your ISP’s server should be suitable):
[mail function]
; For Win32 only.
SMTP = mail.myisp.com
smtp_port = 25
; For Win32 only.
sendmail_from = my@emailaddress.com
Step 4: Add C:\php to the path environment variable
To ensure Windows can find PHP, you need to change the path environment variable. Open Settings, type ‘environment variables’ into the search field and open the result. Select the “Advanced” tab, and click the “Environment Variables” button.
Scroll down the System variables list and click on “Path” followed by the “Edit” button. Click “Edit text” and add ;C:\php to the end of the Variable value line (remember the semicolon).
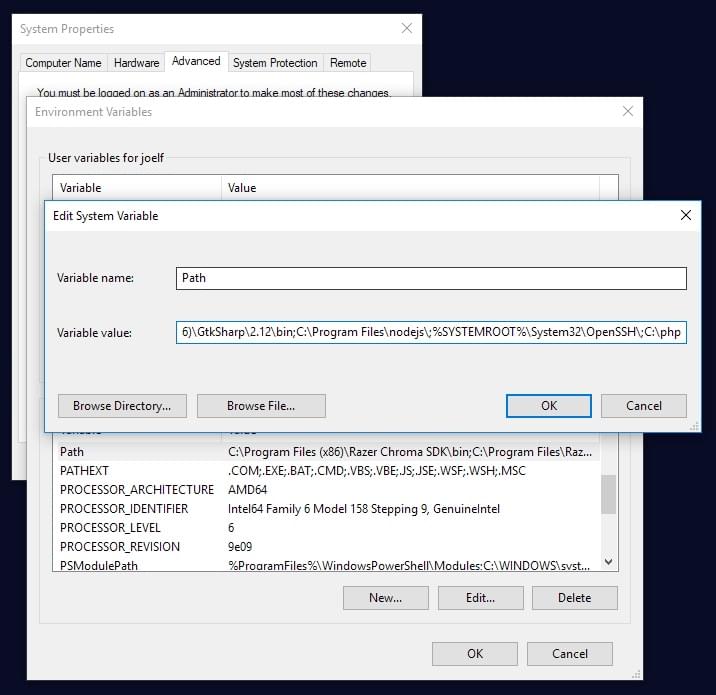
Now click OK until you’re out. You might need to reboot at this stage.
Step 5: Configure PHP as an Apache module
Ensure Apache is not running (use net stop Apache2.2 from the command line) and open its confhttpd.conf configuration file in an editor. The following lines should be changed:
On line 239, add index.php as a default file name:
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html
At the bottom of the file, add the following lines (change the PHP file locations if necessary):
# PHP5 module
LoadModule php5_module "c:/php/php5apache2_2.dll"
AddType application/x-httpd-php .php
PHPIniDir "C:/php"
Save the configuration file and test it from the command line (Start > Run > cmd):
cd Apache2bin
httpd -t
Step 6: Test a PHP file
Create a file named index.php in Apache’s web page root (either htdocs or D:WebPages) and add this code:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Ensure Apache has started successfully, open a web browser and enter the address http://localhost/. If all goes well, a “PHP version” page should appear showing all the configuration settings.

